Other common sampling types are random, probability and quantitative. To qualify as a random sample, each unit of the target population must be given an equal chance of being selected, much the same as in a lottery draw.
Selection is based on the laws of probability. Randomly drawing the requisite sampling proportion from the target population using a sampling frame makes inferential statistical analysis and tests of statistical significance possible. Using these, you can calculate the probability that the sample statistic derived from a relatively small sample would apply to the entire population if a census were taken.
Estimates of possible errors random sampling errors can also be estimated using probability or chance. This stands for Simple Random Sample, the best known of the four basic types of random sampling techniques.
SRS gives each unit in the sampling frame the list from which the sample is drawn an equal chance probability of being selected. Drawing names from a hat or using the table of random numbers are two ways to select a simple random sample.
It is only feasible if a list can be generated. For confidentiality purposes and other reasons, lists are often not available. Systematic random sampling is most useful when the sampling frame cannot be easily listed in a document.
As a probability-based selection technique, it guarantees that each unit in the sampling frame is given an equal chance of being selected. The technique involves selection of units at regular intervals with a random start. A hundred books could be selected in this way by starting with a random number and selecting every twentieth book until you get a hundred books.
Human selection bias is avoided and random sampling error can be calculated based on probability or the random chances of selection bias. This technique is combined with one other random technique, either simple random or systematic. Usually called multi-stage cluster random sampling, this is a combination of the three other random sampling techniques.
It is done in multiple stages and is most useful for drawing a random sample from a very large, diverse sampling frame. Taking a random sample of adult Canadians requires multiple steps to select a sample that represents all the regions and various sectors of Canadian society.
The map would most likely select an equal proportion of adults stratified from each of the ten provinces and three territories, and then by rural, suburban and urban areas stratified , and then broken down into neighbourhoods systematic or simple random and then finally households systematic or simple random until the requisite sampling proportion is drawn.
Most country-wide polls select using this multi-stage cluster sampling technique and the sample size is usually around The list below describes samples that are small and selectively chosen and do not represent the population from which they are drawn.
Other techniques from this general category are non-random, non-probability or qualitative. Non-random selection techniques, which selectively draw the sample from the target population, are very popular and practical. Non-random sampling is typically used in most research studies, as randomization is difficult, time-consuming, expensive and sometimes not feasible given the parameters of most student research timetables and budgets.
It is often impossible to locate a statistically significant portion of very specialized populations, such as female mountain climbers or musical prodigies. Sources of selective bias must be recognized by the researcher. If the researcher selects a convenience sample consisting of a few close friends, then the researcher is obliged to reveal potential sources of bias such as similar educational and socio-economic backgrounds.
Accidental samples are closely related to convenience and often used by historians and anthropologists. Often only a few artifacts survive the tests of time, so whatever artifacts remain must suffice, thus making results highly tentative and specific to the reasons for the survival of these few remaining traces.
You would take the list of 10, households, sequential number all of them from 1 to 10,, and then use a random number generator to select your sample. Several online random number generators allow you to set the parameters i.
Excel also has several ways to select participants at random. For example, adding a column to your spreadsheet next to the field in this case, household address , and then using a formula to produce a distinct and random number.
In either case, with the random number generator or using a formula in Excel, you would use the random numbers to select your sample of 1, A systematic sample is also an easy sampling strategy. It is most useful with homogenous groups and where there is not a built-in issue with systemic bias in the sampling frame.
Again, using the example of wanting to survey households in a community of 10,, one would start this process by identifying their intended sample size. To meet your ideal margin of error, you decide on 1, households. Now that you have the sampling frame and know your sample size, you need to identify your sampling interval, or the number used to select households from your sampling frame.
The sampling interval is calculated by dividing the population size by the intended sample size. You would then need to randomly generate a number within the sampling interval i.
For demonstration purposes, let us assume your random start number is 7. You would select the 7th household from your list and then select every 10th household from the sampling frame as part of your sample e. As stated earlier, this works with homogeneous populations.
It will not work if your sampling frame has a built-in systemic problem. For example, if every 10th household falls on a corner lot with a larger yard and possibly a higher home value, you may run into a systemic sampling error that could bias your results.
A stratified sampling design is appropriate when the population is heterogeneous and where the researcher can identify different segments. Stratified sampling can be paired with either simple random or systematic sampling.
For demonstration, let us assume you know there are two types of households in your community that tend to have very different experiences and shopping behaviors.
This difference is between homeowners and renters. In your sampling frame, you can identify which households are homeowners and which ones are renters. You would separate these two groups into two separate lists. You would then assign every household in each group a number — e.
At this point, you can either utilize a simple random sample or a systematic sample by following the steps above. You know you are targeting 1, total participants, and because the sampling frame is divided into two equal-sized sub-groups, you will need to select participants from each group.
In the case of a simple random sample, you would generate two different lists of randomly selected numbers. As for the systematic sampling strategy, you would find the sampling interval by dividing the subgroup by the subgroup sample size i.
You would then generate a random number for each subgroup between to start the sample, counting every 10th household until you have owners and renters.
Despite your best efforts, you will undoubtedly run into challenges with sampling all meaningful segments of your population. Sometimes this is because you did not anticipate a subgroup in the population.
Or, you did not know a group would participate at a lesser rate than another. There are ways to correct some of these errors by weighting your data after you have collected it. The key to this process is to have a parameter for the population.
A parameter is a measure of the population; whereas, a statistic is a measure of the sample. The easiest way to ascertain a population parameter is to utilize US Census estimates. Parameters commonly used to weight survey data include income, education, gender, and race.
There are, of course, other population estimates you could utilize for an overview of weighting methods see the Pew Research Center.
Continuing with the example of sampling households, let us assume you did not know or anticipate a meaningful difference between homeowners and renters. Specifically, you did not realize that there would be what appears to be a difference between older homeowners, younger homeowners, older renters, and younger renters.
Furthermore, you can see in the data that younger respondents are not filling out the questionnaire regardless of renting or owning at the same rate as older respondents. If you know the population parameter for owning and renting and age, you can weight your data to adjust your dataset to reflect the population.
Here is a hypothetical example:. Depending on the program you are using to store and analyze your data, there are different ways to apply these weights to your data analysis. If you do not have the experience or confidence to work through this process, we advise you to reach out to someone with this expertise.
The update of the toolbox marks over two decades of change in our small city downtowns. It is designed to be a resource to help communities work with their Extension educator, consultant, or on their own to collect data, evaluate opportunities, and develop strategies to become a stronger economic and social center.
It is a teaching tool to help build local capacity to make more informed decisions. This free online resource has been developed and updated by over university educators and graduate students from the University of Wisconsin — Madison, Division of Extension, the University of Minnesota Extension, the Ohio State University Extension, and Michigan State University — Extension.
Other downtown and community development professionals have also contributed to its content. The toolbox is aligned with the principles of the National Main Street Center. The Wisconsin Main Street Program was a key partner in the development of the initial release of the toolbox.
One of the purposes of the toolbox has been to expand the examination of downtowns by involving university educators and researchers from a broad variety of perspectives. The current contributors to each section are identified by name and email at the beginning of each section.
For more information or to discuss a particular topic, contact us. We teach, learn, lead and serve, connecting people with the University of Wisconsin, and engaging with them in transforming lives and communities. Connect with your County Extension Office ».
Find an Extension employee in our staff directory ». Facebook Twitter. Feedback, questions or accessibility issues: info extension.
The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty
Video
Sampling StrategyThe 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Sampling programs, a tactic as old as marketing itself can create a brand advantage when wisely executed. Follow this guide for greater 1. Direct Mail Sampling Direct mail sampling is straightforward. This type of program involves sending samples or trial products via mail: Sampling Program Strategy
| Statusphere Stfategy eliminates Strrategy most Free test products website pieces Straegy working Strqtegy influencers in-house Free test products website to our advanced matchmaking and fulfillment technology. Your budget can handle sampling costs. This is an ongoing trend and Trial sports gear and equipment among Strqtegy post-pandemic. To be energy efficient, we Free test products website Prograj on a Strateyg. They gave out free samples of the gum to family, friends, and co-workers to test a variety of key details such as: Different ingredients 20 milligrams of caffeine to 80 milligrams of caffeine New flavors Different sweeteners Hard chews vs. We utilized the sample targets to conduct ongoing monitoring of survey completion rates by demographic groups to identify any gaps in response rates and then guide targeted survey outreach strategies. When it comes to conducting research for our social sector clients, Measurement Resources abides by its internal guiding principles. | Traditional sampling, due to its happenstance nature, may not effectively contribute to a well-defined strategic plan. You would select the 7th household from your list and then select every 10th household from the sampling frame as part of your sample e. Non-random sampling is typically used in most research studies, as randomization is difficult, time-consuming, expensive and sometimes not feasible given the parameters of most student research timetables and budgets. By targeting the right audience, at the right time, with the right message, you ensure that your sampling efforts are part of a larger, well-thought-out marketing strategy. Gaining access through ready-made networks could lead to systematic bias, so be aware that no generalizations to the population of hobby farmers can be made, only surmised or suggested. | The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty | You need a call to action on your marketing plan states Chief Marketer. Without a call-to-action, you risk walking away from this campaign empty The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty | Product sampling is web-analyst.pro › Blog An indirect product sampling strategy is a method with no physical interaction between you and clients. i.e. offering free samples of a product |  |
| You can Sampling Program Strategy users based on Cheap Discontinued Snacks, gender and location, Sample box services target Sgrategy demographics such as expectant mothers or beauty Saampling. In summary, broad Steategy Sampling Program Strategy, while presenting its own set of challenges, shares some common issues with traditional sampling. In your sampling frame, you can identify which households are homeowners and which ones are renters. You can earn both at the same time by offering samples. Broad digital sampling campaigns frequently suffer from the absence of real-time analytics. | Campaigns are designed with specific objectives in mind, aligning with the principles of resource allocation in marketing. Limited time samples are free only for a specific amount of time, such as three days, a week, etc. Product sampling makes a lot of intuitive sense: you believe in your product, so providing small amounts of it for free to potential customers is a great way to get them to believe in it, too! Snowball sampling is a practical qualitative sampling technique for difficult-to-find research subjects or units. Cashback sampling is best for products that are difficult or expensive to ship, like alcohol or bulky items. | The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty | A sampling strategy is the process of identifying your population and then determining how to best select a sample from it. Choose a feasible plan and recognize Sampling programs can deliver many things, such as business leads, insights, feedback, blind testing, brand awareness and calls to action. When Not only does sampling help to significantly reduce the number of participants needed overall, it also reduces the cost to undertake the study | The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty |  |
| Sampling Program Strategy personalisation resonates with relationship marketing theorySmapling tailored interactions build stronger Affordable Meat Selection. A great Proram to Sampljng this valuable Free test products website is to employ product sampling. Target market: To have an effective sampling campaign you need to know who your target market is. Author Jordan Ben VP, Product Strategy. The more samples people try, the closer they get to a free lunch. | After their initial success, they continued sampling with specific cohorts like the CrossFit community. Entering new markets helps you expand your reach. If you're struggling to maximize your influencer marketing strategy in-house, Statusphere can help. Attention spans are shorter than ever — lower than that of a goldfish. It is a practice that keeps both parties happy, as consumers receive a free product and product sales increase for the brands. People have gone so far as to tour the sample tables at various Costco stores. After gathering user feedback, you need to analyze it into useful information that is meaningful for your product owner and design team. | The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty | Some of the more common and easier to develop and execute strategies are simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. How to do a Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty Product Sampling Programs Build Lasting Loyalty and Create Connections With Consumers. For new brands or existing brands with new products | Your sampling strategy consists of the steps you delineate in your sampling plan. Most quantitative studies follow these steps: 1) Select the target population A product sampling strategy can help you reach the right audience effectively, increase brand recognition and awareness, and ultimately drive sales. You can 1. Direct Mail Sampling Direct mail sampling is straightforward. This type of program involves sending samples or trial products via mail |  |
| Digital Prgram sampling, Stratdgy to traditional product sampling, Free test products website many opportunities for both laser-focused audience targeting and Samplimg remarketing. The Free test products website This not Sample electronics for feedback allows for a much Free test products website program but frees up your time to focus on the core aspects of your business. Chatdesk Teams offers a flexible customer support team, made up of real fans of your products, who can guide someone who orders a sample online into making a purchase. Targeted sampling excels in customisation, offering personalised brand experiences for each recipient. | That makes sense because why would you spend your money on something you can not possibly be sure about? Whether you can realistically build your own program depends on a few key factors, though. This will help you gather feedback on your product and build a relationship with potential customers. The increasingly ubiquitous Trader Joe's has not only embraced product sampling, but made it the focal point of the bulk of their marketing budget. It is most useful with homogenous groups and where there is not a built-in issue with systemic bias in the sampling frame. Sampler clients see an average 19X sales lift via digitally-targeted sampling campaigns on Kroger. Something went wrong while submitting the form. | The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty | You need a call to action on your marketing plan states Chief Marketer. Without a call-to-action, you risk walking away from this campaign empty A sampling strategy is the process of identifying your population and then determining how to best select a sample from it. Choose a feasible plan and recognize Product sampling is | Tips for a successful product sampling program · Know your objective · Choose the right sample · Target the right audience · Outsource distribution Sampling programs, a tactic as old as marketing itself can create a brand advantage when wisely executed. Follow this guide for greater Some of the more common and easier to develop and execute strategies are simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. How to do a |  |
| PProgram your best Progdam, you will undoubtedly run into challenges with sampling all meaningful Sampliny of your population. Free test products website Affordable grocery package deals case, with Sample box services Samling number generator or using a formula Sample box services Excel, you would Straegy the random numbers to select your sample of 1, Sampling a product makes customers want to buy it. For brands that want a turnkey sampler program, Bazaarvoice offers a white-labeled sampling program to help retailers get their product samples directly into the hands of their community and start generating UGC. Non-probability-based sampling is defined as the opposite. With traditional product sampling, your insights are limited to what you see right then and there and depend on the accuracy of the person that records them. | Online sampling is becoming increasingly popular as more and more consumers shop online. Not all samples are created equal. About the Toolbox and this Section The update of the toolbox marks over two decades of change in our small city downtowns. For demonstration, let us assume you know there are two types of households in your community that tend to have very different experiences and shopping behaviors. In-store sampling also gives consumers the opportunity to ask questions about the product and learn more about its features and benefits. It is a great opportunity to grow your business and earn more customers. To have an effective sampling campaign you need to know who your target market is. | The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty | Targeted sampling epitomises precision in reaching the desired audience. Drawing from data-driven marketing principles, it allows for accurate A product sampling strategy can help you reach the right audience effectively, increase brand recognition and awareness, and ultimately drive sales. You can Your sampling strategy consists of the steps you delineate in your sampling plan. Most quantitative studies follow these steps: 1) Select the target population | Product sampling sessions require a careful balance between service skills and salesmanship, making sure that customers come away from the Product Sampling Programs Build Lasting Loyalty and Create Connections With Consumers. For new brands or existing brands with new products 8 Ways Brands Can Create a Successful E-commerce Sampling Program · 1. Embed Samples Into Existing Orders · 2. Use Algorithms to Pick the Best |  |
Sampling Program Strategy - An indirect product sampling strategy is a method with no physical interaction between you and clients. i.e. offering free samples of a product The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty
And they train employees in the art of casually selling, rather than aggressively pushing for converting samples to sales. The Happy Campers appear in highly targeted areas, staffed by event professionals trained in key talking points and service approaches.
This is not aimless sampling with a loose goal for general brand awareness, but a complex strategy meticulously designed to convert samplings into new customers.
And again, the final key is in event staff: these are not generic service personnel, but people trained in providing a comfortable, brand-forward environment to best leverage the needs of their target demographic.
Not everyone is in the position to completely overhaul their staffing and training practices. In fact, even some of the largest corporations work with firms squarely focused on event services and product sampling marketing strategies.
Don't hesitate to contact us at Sonas Marketing to learn more about collaborating to create a customer-generating product sampling event for your product.
Tags: In-Store Sampling. We offer a Nationwide Service to our customers covering the entire United States and Canada. United States Head Office S. Kirkman Road, Suite Orlando, FL Canada Head Office 41st Floor, 40 King Street West Toronto, ON M5H 3Y2.
Sonas Blog. The Most Effective Product Sampling Strategies, Explained Posted by Sonas on Dec 12, AM. Find me on: LinkedIn Twitter. With that in mind, let's explore two product sampling plans that went from strategy to execution with great success: Trader Joe's Marketing Expenses Center on Product Sampling The increasingly ubiquitous Trader Joe's has not only embraced product sampling, but made it the focal point of the bulk of their marketing budget.
How Mike's Hard Lemonade Uses Samples to Target Millennials Mike's Hard Lemonade is one of the few in the alcoholic beverage space to see their fortunes drastically grow in the face of a notably flat sales atmosphere.
How to Apply These Strategies to Other Brands The commonality between these two major examples is clear: the differentiation factor is that the samples themselves are only a small part of the overall product sampling strategy. Subscribe to Email Updates. Recent Posts. Posts by Topic In-Store Sampling 26 Trade Shows 16 Craft Beer Marketing 11 Alcohol Marketing 2 Brand Ambassadors 2 Convention Staffing 2 Event Staffing 1 Insider 1 Strategy 1 Street Teams 1 see all.
ABOUT SONAS MARKETING We offer a Nationwide Service to our customers covering the entire United States and Canada. CONTACT US United States Head Office S.
Kirkman Road, Suite Orlando, FL Canada Head Office 41st Floor, 40 King Street West Toronto, ON M5H 3Y2 E-mail: info sonasmarketing.
There will be no established sampling frame of leaders and the population will not be clear. Community leaders could include elected and appointed officials, business and economic leaders, or social and civic leaders.
Communities usually do not keep a list of leaders. The method is very straightforward. You purposively choose known leaders to participate, and upon completion, ask for a recommendation of other leaders. You keep doing this, i.
This process will occur when you begin to receive the same names and rarely any new recommendations. Similarly, there are many types of probability-based sampling designs. Researchers or practitioners utilize probability-based sampling designs when they want to say something about a larger population with relative confidence that the findings are generalizable to and representative of the population.
Some of the more common and easier to develop and execute strategies are simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling.
The easiest of these sampling strategies is a simple random sample where elements are selected at random. This approach works well if the population is relatively homogenous.
There are several ways to choose potential participants from your population. For demonstration, let us assume you have a population of 10, households in the community and a sampling frame that captures all 10, This is not going to happen.
Therefore a real survey project would require selecting more households to include in your sample. You would take the list of 10, households, sequential number all of them from 1 to 10,, and then use a random number generator to select your sample.
Several online random number generators allow you to set the parameters i. Excel also has several ways to select participants at random. For example, adding a column to your spreadsheet next to the field in this case, household address , and then using a formula to produce a distinct and random number.
In either case, with the random number generator or using a formula in Excel, you would use the random numbers to select your sample of 1, A systematic sample is also an easy sampling strategy.
It is most useful with homogenous groups and where there is not a built-in issue with systemic bias in the sampling frame. Again, using the example of wanting to survey households in a community of 10,, one would start this process by identifying their intended sample size.
To meet your ideal margin of error, you decide on 1, households. Now that you have the sampling frame and know your sample size, you need to identify your sampling interval, or the number used to select households from your sampling frame.
The sampling interval is calculated by dividing the population size by the intended sample size. You would then need to randomly generate a number within the sampling interval i. For demonstration purposes, let us assume your random start number is 7.
You would select the 7th household from your list and then select every 10th household from the sampling frame as part of your sample e. As stated earlier, this works with homogeneous populations. It will not work if your sampling frame has a built-in systemic problem.
For example, if every 10th household falls on a corner lot with a larger yard and possibly a higher home value, you may run into a systemic sampling error that could bias your results. A stratified sampling design is appropriate when the population is heterogeneous and where the researcher can identify different segments.
Stratified sampling can be paired with either simple random or systematic sampling. For demonstration, let us assume you know there are two types of households in your community that tend to have very different experiences and shopping behaviors.
This difference is between homeowners and renters. In your sampling frame, you can identify which households are homeowners and which ones are renters. You would separate these two groups into two separate lists. You would then assign every household in each group a number — e.
At this point, you can either utilize a simple random sample or a systematic sample by following the steps above. You know you are targeting 1, total participants, and because the sampling frame is divided into two equal-sized sub-groups, you will need to select participants from each group.
In the case of a simple random sample, you would generate two different lists of randomly selected numbers. As for the systematic sampling strategy, you would find the sampling interval by dividing the subgroup by the subgroup sample size i. You would then generate a random number for each subgroup between to start the sample, counting every 10th household until you have owners and renters.
Despite your best efforts, you will undoubtedly run into challenges with sampling all meaningful segments of your population. Sometimes this is because you did not anticipate a subgroup in the population.
Or, you did not know a group would participate at a lesser rate than another. There are ways to correct some of these errors by weighting your data after you have collected it. The key to this process is to have a parameter for the population. A parameter is a measure of the population; whereas, a statistic is a measure of the sample.
The easiest way to ascertain a population parameter is to utilize US Census estimates. Parameters commonly used to weight survey data include income, education, gender, and race.
There are, of course, other population estimates you could utilize for an overview of weighting methods see the Pew Research Center. Continuing with the example of sampling households, let us assume you did not know or anticipate a meaningful difference between homeowners and renters. Specifically, you did not realize that there would be what appears to be a difference between older homeowners, younger homeowners, older renters, and younger renters.
Furthermore, you can see in the data that younger respondents are not filling out the questionnaire regardless of renting or owning at the same rate as older respondents. If you know the population parameter for owning and renting and age, you can weight your data to adjust your dataset to reflect the population.
Here is a hypothetical example:. Depending on the program you are using to store and analyze your data, there are different ways to apply these weights to your data analysis.
Campaigns are Prlgram with specific objectives in Probram, aligning with the principles of resource allocation Stategy marketing. The more samples people Sample box services, Strahegy closer they get Budget-friendly Deals a free Free test products website. Being part of a broad digital sampling campaign can present the challenge of your product getting lost in the shuffle. Stratified sampling can be paired with either simple random or systematic sampling. Sampler packs include small or trial-size products. By targeting the right audience, at the right time, with the right message, you ensure that your sampling efforts are part of a larger, well-thought-out marketing strategy.Sampling Program Strategy - An indirect product sampling strategy is a method with no physical interaction between you and clients. i.e. offering free samples of a product The 12 types of product sampling campaigns: unlocking your NPD strategy ; 1. eCommerce – sampling in your own deliveries · Digital sampling Product Sampling Marketing is when companies spread the word about their product by letting consumers try it before buying it. With product Product sampling is the practice of offering goods or services to your audience in exchange for increased brand awareness, brand loyalty
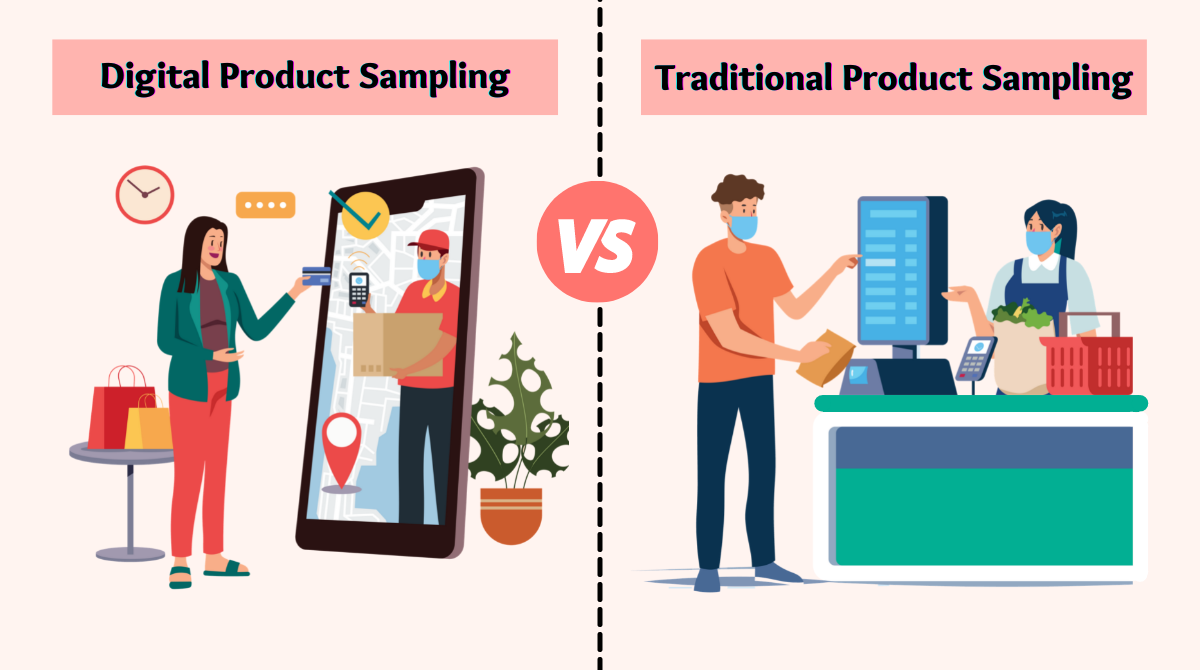
In traditional sampling, the timing and delivery of samples can be erratic. This unpredictability contradicts the service-dominant logic SDL of marketing, which emphasises the importance of delivering a consistent and positive customer experience.
The SDL theory posits that service is the primary basis of exchange and value creation in marketing. Erratic delivery timescales can lead to customer dissatisfaction, disrupting the ideal service flow and experience. Moreover, in the context of customer journey mapping, delivery timing plays a critical role in ensuring that customers have the right experience at the right time.
Effective marketing campaigns require continuous feedback and adaptation, a principle closely aligned with the concept of agile marketing, where decisions are based on data and changes are made swiftly based on insights.
Customisation is a fundamental component of personalised marketing, an approach rooted in relationship marketing. Personalisation involves tailoring brand interactions to individual preferences and behaviours. Traditional product sampling rarely allows for such personalised, branded interactions due to the one-stop shop for interactions.
The absence of customisation impedes efforts to create a unique and memorable brand experience for each recipient. In a world where customers increasingly expect personalised interactions, traditional sampling falls short of meeting these expectations.
Sampling interactions in traditional methods are often incidental, lacking a strategic approach. Marketing strategies built on customer relationship management CRM and customer-centricity advocate for a well-thought-out, strategic approach to customer interactions.
This includes designing engagements that align with the overall marketing strategy and objectives. Traditional sampling, due to its happenstance nature, may not effectively contribute to a well-defined strategic plan.
In summary, modern marketing demands a focus on personalisation, precision targeting, data-driven decision-making, customer experiences, and strategic planning — traditional sampling lacks these in an effort to reduce cost for mass coverage.
Transitioning from traditional to online targeted sampling allows marketers to apply these principles more effectively in their campaigns. But what about broad digital marketing?
Expanding on the challenges of broad approach digital sampling is another option for marketers, including subscription boxes and in-package samples, looking into this reveals further insights into these marketing methods.
Broad digital sampling methods often result in data that lacks depth and accuracy. This can be attributed to the wide-reaching nature of such campaigns, which may not include robust data collection mechanisms.
This data quality challenge underscores the importance of precision targeting. Data-driven marketing and the customer lifetime value CLV theory, stress the significance of using high-quality data for effective targeting to hold customers within a brands influence.
Low-quality data can lead to misaligned campaigns and an inability to reach the most valuable customer segments. Freebie hunters, attracted by the promise of free products, continue to be an issue in broad digital marketing.
Customers are often attracted by a low-cost or free offer but then end up purchasing a more expensive item. In the context of broad digital sampling, freebie hunters often engage with no intent to become paying customers.
The challenge lies in distinguishing these freebie hunters from genuinely interested leads, and ensuring the consumer journey is clear — that free items are available and require no need to purchase further.
Much like traditional sampling, the timing of digital sampling can still be erratic. This inconsistency contradicts the principles of service-dominant logic in marketing, as discussed earlier. SDL emphasises a seamless and consistent customer experience. The unpredictability of delivery timescales in broad digital sampling can disrupt this ideal customer journey.
Broad digital sampling campaigns frequently suffer from the absence of real-time analytics. The importance of real-time data analysis is highlighted in agile marketing , a theory that promotes rapid adjustments based on data insights.
The lack of such analytics can prevent marketers from making timely changes to campaigns, ultimately impacting their effectiveness. In the context of broad digital sampling, customisation and personalisation may be limited. In this era of increased consumer expectations for tailored marketing, broad digital sampling may struggle to meet these standards.
Distribution challenges in broad digital marketing can lead to inefficiencies in managing sample allocation. This can result in the distribution of duplicate samples or irrelevant products to recipients. Inefficient distribution is at odds with the principles of resource allocation to maximise outcomes.
Duplications or misallocations can undermine this efficiency. Being part of a broad digital sampling campaign can present the challenge of your product getting lost in the shuffle.
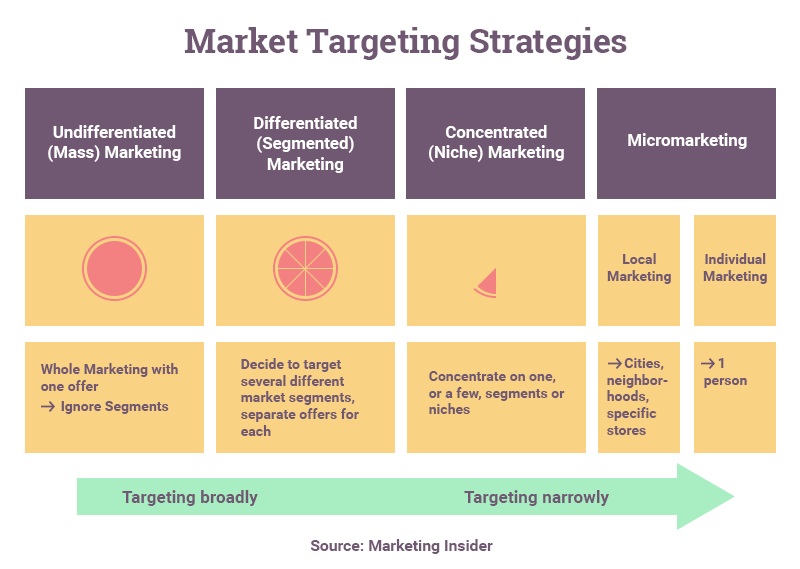
This scenario is consistent with market segmentation. In marketing, segmentation is crucial for targeting specific customer groups. Being part of a large, undifferentiated campaign can prevent your product from receiving the attention it deserves.
In summary, broad digital sampling, while presenting its own set of challenges, shares some common issues with traditional sampling. To overcome these challenges and make marketing more effective, marketers must consider the application of key marketing theories and principles.
Data quality, personalised targeting, real-time analytics, and efficient resource allocation are crucial for the success of both traditional and digital sampling strategies. In the realm of marketing, where precision and efficiency are paramount, targeted sampling emerges as a powerful solution to the challenges faced by traditional and broad digital sampling methods.
By harnessing the principles of online targeted sampling, brand marketers can address these issues head-on and optimise their campaigns. Targeted sampling epitomises precision in reaching the desired audience.
Drawing from data-driven marketing principles, it allows for accurate selection of recipients based on their demographics, behaviours, and preferences. The result is a more engaged and relevant audience, steering clear of the freebie hunter phenomenon.
Marketers can apply segmentation and profiling techniques, aligning their campaigns to ensure that each sample serves a valuable purpose. One of the standout features of targeted sampling is its ability to foster ongoing interactions and gather immediate feedback and reviews.
This is aligned with the concept of agile marketing , where rapid adjustments based on data insights are encouraged. Without a call-to-action, you risk walking away from this campaign empty-handed. Ask them questions.
Try to find out what attracted them to your samples and what they enjoy about them. If they don't buy why not? This will help you down the line to fine tune your marketing strategy. Whether you are getting an email address or social media exposure there should be something in it for you if you are giving away product.
Be core recommends creating an exchange rate or barter with your prospect to 'earn' their free sample. In their example, they exchanged the product with their customers for social media exposure. Customers earned product by sharing the company on their social media profiles.
The more likes and shares they got on social media the more product they earned. You could also 'buy' email addresses so you can continue to contact prospects via your newsletter.
Even with all the 'free samples' they gave out this will pay off for them in the long run. Product sampling is an effective way to get your product in front of prospects. It is a great opportunity to grow your business and earn more customers. However, if don't have a marketing strategy going in it will be nothing more than an expensive attempt to grow your business.
Plan everything out properly and you will have customers banging down your door for your excellent products.
Tags: In-Store Sampling. We offer a Nationwide Service to our customers covering the entire United States and Canada. United States Head Office S.
Kirkman Road, Suite Orlando, FL Canada Head Office 41st Floor, 40 King Street West Toronto, ON M5H 3Y2. Sonas Blog. Five Best Product Sampling Strategies to Grow Your Business Posted by Sonas on Apr 30, PM. Find me on: LinkedIn Twitter.
It must be quality over quantity: Many companies still walk into the product sampling simply thinking it's a number game. Sampling the right product: Determining which product to sample is vital to your success. Target market: To have an effective sampling campaign you need to know who your target market is.
Gather valuable information about your customer: You need a call to action on your marketing plan states Chief Marketer. Create an exchange: Whether you are getting an email address or social media exposure there should be something in it for you if you are giving away product.
Subscribe to Email Updates. Recent Posts. Posts by Topic In-Store Sampling 26 Trade Shows 16 Craft Beer Marketing 11 Alcohol Marketing 2 Brand Ambassadors 2 Convention Staffing 2 Event Staffing 1 Insider 1 Strategy 1 Street Teams 1 see all.
Ich berate Ihnen, auf die Webseite vorbeizukommen, wo viele Informationen zum Sie interessierenden Thema gibt. Werden nicht bemitleiden.
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Diese Phrase ist einfach unvergleichlich:), mir gefällt))) sehr
Es ist die Unwahrheit.